New possibilities of PowerShell in Windows Server 2016
 Kind time of days of %HabraUser%! Not so long ago, I was fortunate to become the owner of VDS with pre-installed Windows Server 2016 to familiarize themselves with the operating system and its new features. Due to the fact that the last few years I've been a fan of the administration using PowerShell, first I was interested in it, as it is used in their daily work to automate routine tasks. In a corporate environment, today most often used the latest version of the operating systems Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, and I didn't pay attention to the changes that brought me Windows 10 on your home computer, and as it turned out nothing. I miss the past itself, the updated tool has become much better, easier and faster compared to previous versions, these major changes and I would like to talk. Welcome to under the cat.
Kind time of days of %HabraUser%! Not so long ago, I was fortunate to become the owner of VDS with pre-installed Windows Server 2016 to familiarize themselves with the operating system and its new features. Due to the fact that the last few years I've been a fan of the administration using PowerShell, first I was interested in it, as it is used in their daily work to automate routine tasks. In a corporate environment, today most often used the latest version of the operating systems Windows 8.1 and Windows Server 2012 R2, and I didn't pay attention to the changes that brought me Windows 10 on your home computer, and as it turned out nothing. I miss the past itself, the updated tool has become much better, easier and faster compared to previous versions, these major changes and I would like to talk. Welcome to under the cat.In the beginning of the list are the minor changes are designed to make daily use of this product more comfortable for the administrator:
the
-
the
- the editor Window PowerShell you can now change the size, dubious achievement, but now to expand the window to full screen;
Let's compare:
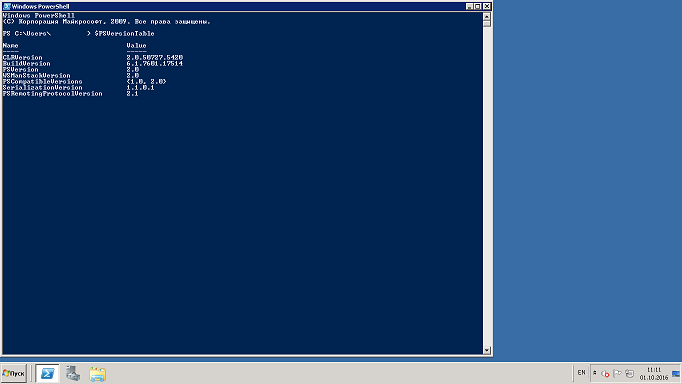
the PowerShell 2.0
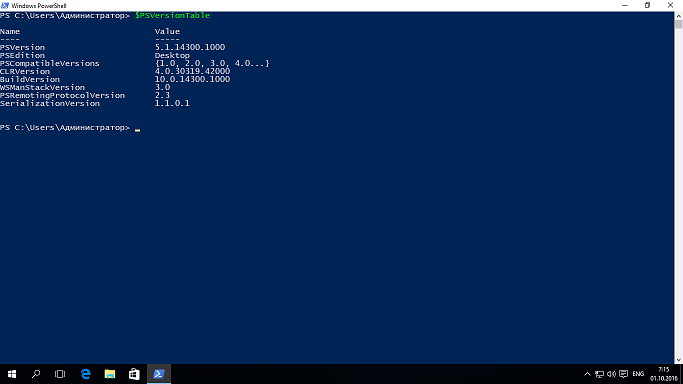
the PowerShell 5.1
- There are classes on this subject there is a separate article;
the - Increased speed of working with com objects.
the Next obvious difference which can be seen in the screenshots is syntax highlighting, but this is a very big plus;
followed by another innovation — today and tomorrow must be supported by modules and cmdlets different versions;
This example is best considered in the screenshots:

the PowerShell 2.0

the PowerShell 5.1
As you can see from the screenshot there is a new team, as well as the more famous earlier Update-Help to update the reference, is used to update the versions of modules Update Module.
the
About the last point I would like to talk separately. The size of the Active Directory in different organizations, there were cases when it was 20-60 users, and was when more than a few tens of thousands and if in the first case, you can do only GUI, in the second it can be done, but quite difficult. Few administrators imagine Active Directory as an extensive information database from which to obtain the necessary data in a matter of minutes by applying to it the correct approach.
Little advertising
Windows Server 2016 only yesterday appeared to download in the catalogue of Microsoft partners and we can already see all the features for just 250 rubles for vpsville.
digression...
Microsoft was initially presented with Active Directory as a tool not only for system administrators but also to the staff of the personnel Department. The first should contain everything in working order from the point of view of server and software architecture, the second is in turn responsible for the correct filling out of the catalogue. Therefore, as is understood from all the sources from which to draw information on this issue, the administrator should not have user accounts, and groups to create the ideology of the Active Directory too, but in our harsh Russian reality all a little not so.
Instead of a specification.
Let's imagine that we are not in the small organization and have under control several domain controllers in branch offices scattered throughout our vast country, respectively, the number of employees we have, for example, will be not less than one thousand people. Remember that the country is divided into many time zones, and when some only come to work others go to sleep, so the model Active Directory management we have a partially centralized, which implies the presence of administrators in the regions, not only in the Central office. We also have internal technical documentation with the requirements of reference Active Directory so that everything was uniform and whether we remember that this is a cool database, and not pow gaffe.
Due to the fact that according to the technical specifications of our data we have very well structured, we can refer to them using standard queries, one example may serve as a directory of employees, which is used at each plant.
So it looks like in PowerShell:
the
Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=Users,OU=Main Office,DC=MyCompany,DC=ru" -Server 'Domain Controller Name' -Properties displayName, description, physicalDeliveryOfficeName, telephoneNumber, mail, title, department, company, manager |
Select displayName, description, physicalDeliveryOfficeName, telephoneNumber, mail, title, department, company, manager |
Export-CSV "C:\Export\MainOffice.csv" -NoType -UseCulture -Encoding Unicodecode Comments
Get-ADUser — the cmdlet which gets an array of users from the scope of the search (-SearchBase) with properties specified using a comma after the parameter -Properties;
Export-CSV — export the array to a file.
Export-CSV — export the array to a file.
In the end we get the finished table with the required fields: full name, office Number, telephone Number, email Address, Position, Name of Department, Name of branch, name of the Head of the employee. This script runs a few seconds and lets us changing total
the
$Template_Excel = "C:\PS\Шаблон.xlsx"
$SaveAs = "C:\PS\ЗаполненыйШаблон.xlsx"
$AllExcel = @(Get-Process [e]xcel | %{$_.Id})
$MyExcel = New-Object -ComObject Excel.Application
$ExcelId = Get-Process excel | %{$_.Id} | Where {$AllExcel -notcontains $_}
$MyExcel.Visible = $False
$WorkBook = $MyExcel.workbooks.open($Template_Excel)
$WorkSheet = $WorkBook.sheets.item("Template")
$Users = Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=Users,OU=Main Office,DC=MyCompany,DC=ru" -Server 'Domain Controller Name' -Properties displayName,
description, physicalDeliveryOfficeName, telephoneNumber, mail, title, department, company, manager |
Select sAMAccountName, displayName, description, physicalDeliveryOfficeName, telephoneNumber, mail, title, department, company, manager
For($x = 0; $x -le $Users.count; $x++)
{
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(1) = $Users[$x].displayName
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(2) = $Users[$x].description
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(3) = $Users[$x].physicalDeliveryOfficeName
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(4) = $Users[$x].telephoneNumber
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(5) = $Users[$x].mail
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(6) = $Users[$x].title
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(7) = $Users[$x].department
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(8) = $Users[$x].company
$WorkSheet.Rows.Item($x+2).Columns.Item(9)= $Users[$x].manager
}
$Workbook.SaveAs($SaveAs)
$MyExcel.quit()
Stop-Process -Id $ExcelId -Force-ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
code Comments
Get-Process — gets the list of processes, in our case, [e]xcel;
New-Object — create a new COM object that runs your Excel process;
Stop-Process — delete the created object.
New-Object — create a new COM object that runs your Excel process;
Stop-Process — delete the created object.
Code in PowerShell has become a little bit more but we got a ready file in which to fix nothing. There was only one big, BUT this code in Windows 8.1 is ~ 25-40 minutes depending on the number of processed objects, and most of the time it takes to work with COM object. Accordingly, this approach used before the emergence of my life PowerShell 5 was uncomfortable because of the time of formation of the file. In Windows 10, or Windows Server 2016 this script fulfills for a few moments allowing you to expand the scope of possibilities.
*
* in the code comments, the cmdlet names are references to the official documentation.
Thanks for reading to the end. Chukcha not the writer, Chukcha the reader.
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий