The perfect catalog, a sketch of the architecture
I found it a task to develop a generic catalog of goods and services, concurrently to the directory, documents and whatever else. In the work of this "experience" is not useful, and the idea is good, in my humble opinion :) I would like to share, and to listen to criticism.
The directory implies an order — a hierarchy directly implies the storage of information, and of course search is probably the dimension... something else? Anything more does not occur.
Now the points.
the
By far the grouping information will be tree-like, abstract from "Catalog" to the more specific, more concrete (e.g. "hammer"). The level of detail can be anything, will not himself to keep within the "section", "subsection", "category", "subcategory", let the branching depth is infinite.
Information will be stored in what DBMS to work with the hierarchy of this DBMS should be able to hierarchical queries, such DBMS is not enough, from free most pop is PostgreSQL.
DDL signs element Tree:
the
the
id — the ID of the table row.
element_tree_id — link to parent tree item.
is_hidden — deleted record flag ( 0 — valid entry, 1 — remote) why write only flag is raised, instead of deleting it? because when I see in the logs the ID and you want to see what it is, it is very convenient to make selelect in the current database, instead of having to do this select in a backup (and not the fact that this stays this record exists).
insert_date — date add record, it is convenient when you know it's 100 year old record or it has inserted five minutes ago as a result of no successful insert.
Of course people who are familiar with it (is_hidden ,insert_date) is not very necessary, but for those who see the system as a RAM on new gate, these fields are very useful in my practice is usually in the role of RAM :)
Fk_element_tree CONSTRAINT — a foreign key to itself is a pointer to the parent element.
Ix_element_tree_element_tree_id_id INDEX — the index to search the child branches (nodes descendants), if the parent we find by primary key, for fast search of descendants we need to have a separate index.
Can see someone experienced and advanced, in the table there is no column for the name element. Why? And because hierarchy is the only hierarchy, and are not the nodes of the tree, and those tables which are docked to the hierarchy, so the names in the tables, in the hierarchy only to group items.
the
Ultimately, any catalog is a list of the individual headings. A category is a group of entities has a unique set of characteristics. That is relevant actually of the Entity and the grouped entity Category, and in addition a Category is a grouping for the unique Characteristics of these Entities.
That is, the information is divided into three parts: Essence, Characteristic, Category, where Category is the point of connection of several Entities and Characteristics.
In the language of the DBMS it is:
Table Headings
the
Table of Entities (something that can be a product or service or company, or even a report and anything else):
the
Article based on information from habrahabr.ru
The directory implies an order — a hierarchy directly implies the storage of information, and of course search is probably the dimension... something else? Anything more does not occur.
Now the points.
the
Hierarchy
By far the grouping information will be tree-like, abstract from "Catalog" to the more specific, more concrete (e.g. "hammer"). The level of detail can be anything, will not himself to keep within the "section", "subsection", "category", "subcategory", let the branching depth is infinite.
Information will be stored in what DBMS to work with the hierarchy of this DBMS should be able to hierarchical queries, such DBMS is not enough, from free most pop is PostgreSQL.
DDL signs element Tree:
the
CREATE TABLE element_tree
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
element_tree_id INTEGER,
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_element_tree CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (element_tree_id) REFERENCES element_tree (id)
);
CREATE INDEX ix_element_tree_element_tree_id_id ON element_tree (element_tree_id, id);
the
explanation of the table structure
id — the ID of the table row.
element_tree_id — link to parent tree item.
is_hidden — deleted record flag ( 0 — valid entry, 1 — remote) why write only flag is raised, instead of deleting it? because when I see in the logs the ID and you want to see what it is, it is very convenient to make selelect in the current database, instead of having to do this select in a backup (and not the fact that this stays this record exists).
insert_date — date add record, it is convenient when you know it's 100 year old record or it has inserted five minutes ago as a result of no successful insert.
Of course people who are familiar with it (is_hidden ,insert_date) is not very necessary, but for those who see the system as a RAM on new gate, these fields are very useful in my practice is usually in the role of RAM :)
Fk_element_tree CONSTRAINT — a foreign key to itself is a pointer to the parent element.
Ix_element_tree_element_tree_id_id INDEX — the index to search the child branches (nodes descendants), if the parent we find by primary key, for fast search of descendants we need to have a separate index.
Can see someone experienced and advanced, in the table there is no column for the name element. Why? And because hierarchy is the only hierarchy, and are not the nodes of the tree, and those tables which are docked to the hierarchy, so the names in the tables, in the hierarchy only to group items.
the
Direct storage
Ultimately, any catalog is a list of the individual headings. A category is a group of entities has a unique set of characteristics. That is relevant actually of the Entity and the grouped entity Category, and in addition a Category is a grouping for the unique Characteristics of these Entities.
That is, the information is divided into three parts: Essence, Characteristic, Category, where Category is the point of connection of several Entities and Characteristics.
In the language of the DBMS it is:
Table Headings
the
CREATE TABLE rubric
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
code CHAR(100),
title VARCHAR(4000),
description VARCHAR(4000),
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_code ON rubric (code);
Table of Entities (something that can be a product or service or company, or even a report and anything else):
the
CREATE TABLE item
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
code CHAR(100),
title VARCHAR(4000),
description VARCHAR(4000),
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_item_code ON item (code);
Table of Characteristics (properties):
the CREATE TABLE property
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
code CHAR(100),
title VARCHAR(4000),
description VARCHAR(4000),
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_property_code ON property (code);
Here we see a new column:
code — unique code (mnemonics) to record, to register the queries and configs, the IDs are not kamilfo, because IDs on different machines to be different and to ensure that they were the same little exhausting, much more convenient to use the record ID — it and easier to remember than a set of numbers of the identifier, and in the code when you see the word, not magic numbers become a little clearer what was going on.
title — the title (name had to be changed to the title because name is a key word for PostgreSql).
description — description ( name used to select it in the list and the description to actually describe the purpose of the record).
Now that everything is connected.
the Organization of information
Headings are snapped to the element tree, dock performed by a separate table:
the CREATE TABLE rubric_element_tree
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rubric_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
element_tree_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_rubric_element_tree_rubric_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (rubric_id) REFERENCES rubric (id),
Fk_rubric_element_tree_element_tree_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (element_tree_id) REFERENCES element_tree (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_element_tree_rubric_id ON rubric_element_tree (rubric_id);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_element_tree_element_tree_id ON rubric_element_tree (element_tree_id);
The table serves as a "one to one" table has two foreign key column for each key has its own index.
The Category and the Element tree can be stykovanii only once, so for each column made the index unique.
Each category has its own set of Characteristics (properties):
the CREATE TABLE rubric_property
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rubric_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
property_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_rubric_property_rubric_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (rubric_id) REFERENCES rubric (id),
Fk_rubric_property_property_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (property_id) REFERENCES property (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_property_rubric_id rubric_property ON (rubric_id, property_id);
CREATE INDEX ix_rubric_property_property_id ON rubric_property (property_id);
The table has two foreign key relationships form one-to-many.
One Column is one Feature one time is provided by the index, different Headings can be one and the same Feature index Feature without the uniqueness of the values.
Each category has its own set of Entities (Pieces):
the CREATE TABLE rubric_item
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
rubric_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
item_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_rubric_item_rubric_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (rubric_id) REFERENCES rubric (id),
Fk_rubric_item_item_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (item_id) REFERENCES item (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_item_rubric_id_item_id rubric_item ON (rubric_id, item_id);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_rubric_item_item_id ON rubric_item (item_id);
The table has two foreign key relationships form one-to-many. One Column multiple Entities, each Entity can belong to only one Category.
It was a structure of data storage, so where's the information?
The information itself is stored separately.
the store information
Table of Values (the value of information characteristics):
the CREATE TABLE content
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
raw VARCHAR(4000),
redactor_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
property_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_content_redactor_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (redactor_id) REFERENCES redactor (id),
Fk_content_property_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (property_id) REFERENCES property (id)
);
CREATE INDEX ix_content_redactor_id ON content (redactor_id);
CREATE INDEX ix_content_property_id ON content (property_id);
This plate is not quite normal, in fact it is just a cell "memory" which stores the value (raw). The value of the specified characteristics (property_id). The value of the specified a specific Editor (redactor_id). From the table it is not clear what attitude the value of this characteristics, whether the model of the hammer, or to the model of the video card, docking with the Essence of this task is a separate table, but this is still too early, need Editors to tell:
the CREATE TABLE redactor
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
code CHAR(100),
description VARCHAR(4000),
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_redactor_code ON redactor (code);
Why do we need an Editor? Catalog information expected something like Wikipedia, where each Editor could ask his version of the values of the Characteristics for each Entity. And actually the System was supposed to work with variations of the Editors to represent the same Entity, considered analysis on these variations.
The Values table stores only a string representation of information about the Characteristics. It is actually user input. The system works with another provision of this information, with the representation depending on the type of data. Each data type has its own table.
Line
the CREATE TABLE string_matter
(
content_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
string VARCHAR(4000),
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_string_matter_content_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_string_matter_content_id ON string_matter (content_id);
*for storing rows in PostgreSql you should use a TEXT
Number
the CREATE TABLE digital_matter
(
content_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
digital DOUBLE PRECISION,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_digital_matter_content_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_digital_matter_content_id ON digital_matter (content_id);
Date (timestamp)
the CREATE TABLE date_matter
(
content_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
date_time TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_date_matter_content_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_date_matter_content_id ON date_matter (content_id);
Time intervals
the CREATE TABLE duration_matter
(
content_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
duration INTERVAL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_duration_matter_content_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_duration_matter_content_id ON duration_matter (content_id);
Data types specifically selected, it was possible to move the structure of the database on any platform, on any database.
The name "matter" is selected for the consonance of the words "matter" and "matter".
And one thing they say, it's options:
the CREATE TABLE option
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
code CHAR(100),
title VARCHAR(4000),
description VARCHAR(4000),
is_hidden INTEGER DEFAULT 0,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now()
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_option_code ON option (code);
Options are necessary as tags, which define how to process Characteristics like for them to carry out Analytics which search engine to use, what type of data to save, what rights (permissions) required to access and all such business logic is tied to the options.
The options correspond with the Characteristics:
the CREATE TABLE property_option
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
property_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
option_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_property_option_property_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (property_id) REFERENCES property (id),
Fk_property_option_option_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (option_id) REFERENCES option (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_property_option_property_id_option_id ON property_option (property_id, option_id);
CREATE INDEX ix_property_option_option_id ON property_option (option_id);
The content connects to Entities:
the CREATE TABLE item_content
(
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
item_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
content_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
insert_date TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE DEFAULT now(),
Fk_item_content_item_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (item_id) REFERENCES item (id),
Fk_item_content_content_id CONSTRAINT FOREIGN KEY (content_id) REFERENCES content (id)
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_item_content_item_id_content_id ON item_content (item_id, content_id);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX ux_item_content_content_id ON item_content (content_id);
Actually it is all component of directory Information.
the Chip "architecture"
Now the main question, what is the number of connecting plates, is it not possible to join tables directly?
The answer is that this "architecture" is aimed at maximum modularity. Each table is tuned for one function and these functions can be flexibly combined. Flexibility is only interrupted by a table of Values — content of course communication with the Editors was to bring in a separate table, but this is too over the edge (although in the following implementation I will do so). The link with the content property hard because the Value (content) is not possible to interpret outside of the characteristic (property).
The flexibility of the linkages done for the convenience of throwing entities among other entities in the System.
We are an entity with the same set of Values can flip between different sections and in each Section we have Entities we see and work only with those Characteristics which are defined for this Column. Can freely transfer Values from one Entity to another, while not affecting the actual values themselves.
Can only use the string representation of information and to forget about the highly specialized performances in tables *_matter.
Can only use Rubrics without spreading Rubrics at the element Tree. And can across the Tree to scatter only those Headings you want to give access to users, and system Heading to the tree is not docked and thus to hide them from users.
For the Headings to add or remove Features, the Values will not hurt and will not be affected.
That is, from project to project can use only the functionality which is needed and which is not needed can be cut in two, simply excluded from the Assembly does not need classes.
In General, you can twist and turn as us data pleases without any changes in the structure of the database, and therefore no change in the classroom working with these data, if you change the logic would have to change only the business layer without changing the data access layer, without changing "primitive" class is responsible for the interface to edit the data.
With increased overhead to access the data, we obtained greater flexibility and greater resistance to the careless actions of the user, it is possible to conduct some experiments without the need for backups, for those "risky" and lazy programmers like me is a big plus :)
To all this "beauty" is still PHP code, but about it next time, and given my "Recovery mode", only in a week.
PS. I guess after your comments I'll have more time about this "architecture" to write, and then you can tell the story of PHP classes for working with this system of storing and processing data.
the ER Diagram
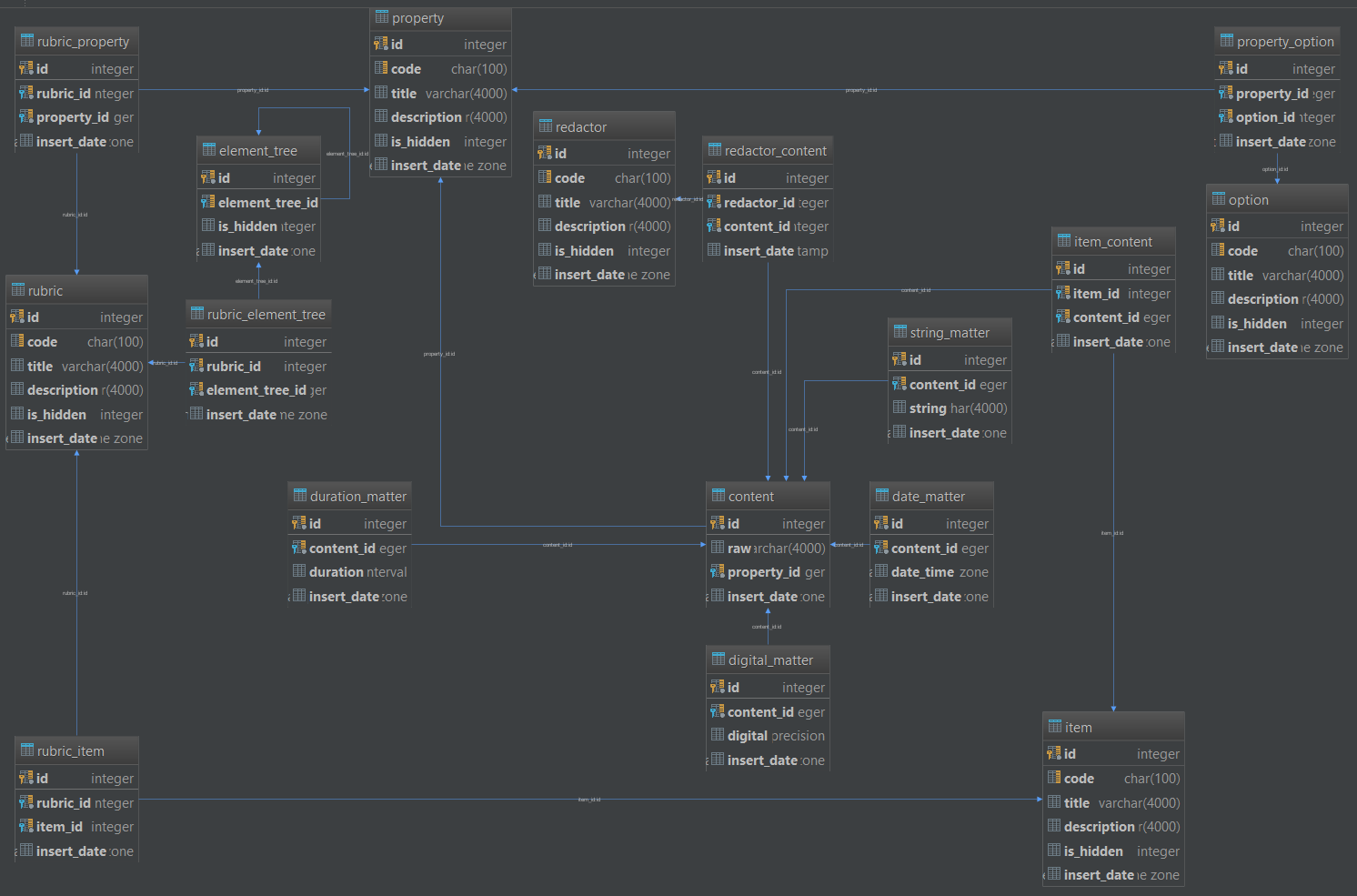
the to be Continued
Perfect directory, sketch of architecture
Комментарии
Отправить комментарий